Web server
The CANedge2 (FW 01.08.01+) lets you interface the SD card via WiFi (no server required). This lets you easily download log files or perform OTA updates via your browser or the REST API.
See the CANedge2 Docs[1] for details - below we provide additional tips and tricks.
Table of Contents
S3 vs web server and router setups

The CANedge2 can be configured to use either the web server or S3 interface. See our web server article for guidance on selecting the best connectivity mode for your use case.
Example setups
Below we provide guidance on some of common deployment setups
Mode 1: Router WiFi AP (local)
You can connect the CANedge2 to an existing WiFi network. With a PC to the same network you can access the device by entering the device IP in your browser as per the Docs[2].
Mode 2: Router WiFi AP (remote + VPN)
You can port forward the device IP to make it accessible remotely via the internet. For security purposes, we recommend using a VPN in this setup.
Mode 3: PC WiFi AP (online)
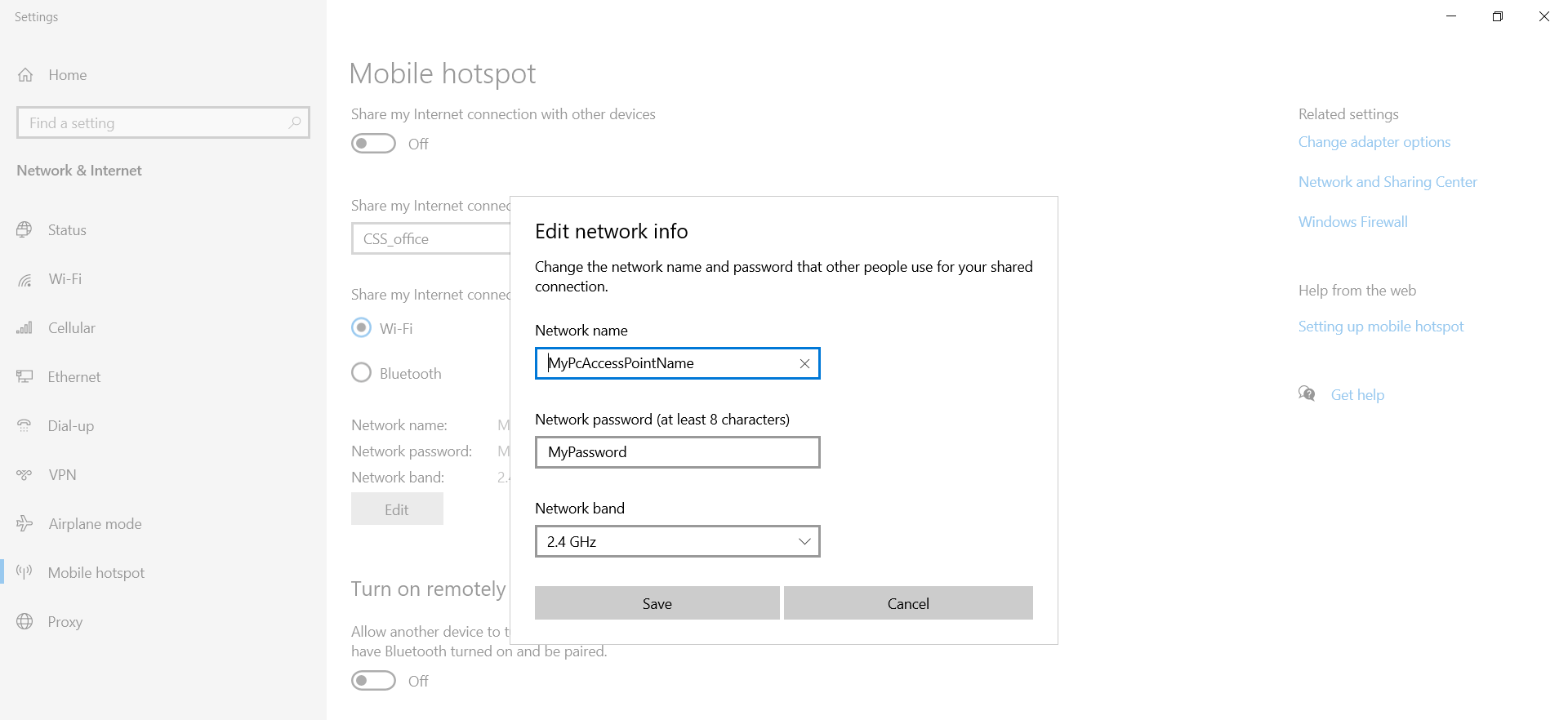
You can set up your laptop to act as a WiFi access point, thus avoiding the need for a separate WiFi router. On Windows 10, this can be done by opening the ‘Mobile Hotspot’ settings and enabling the sharing with your preferred WiFi name/password and using 2.4 GHz. When you have configured the CANedge2 accordingly, its IP will show up as a connected device.
Mode 4: PC WiFi AP (offline)
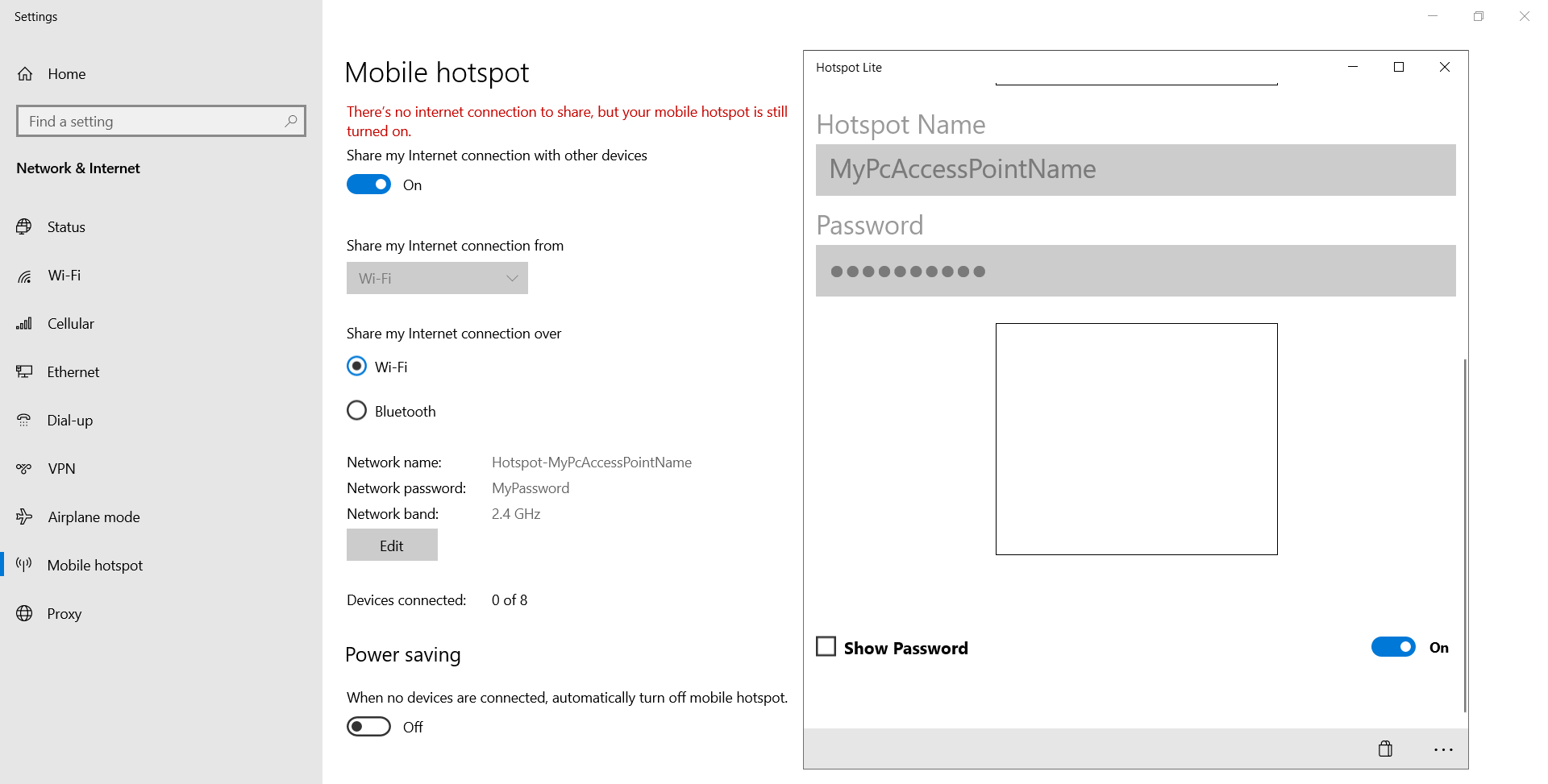
By default, the ‘Mobile Hotspot’ functionality in Windows 10 does not work if your PC is offline. However, you can get around this by installing a free tool called ‘Hotspot Lite’ via the Microsoft Store. This tool lets you ‘force’ Windows to expose a WiFi AP while offline. Once you start the sharing via Hotspot Lite, you will need to go to the Windows 10 Mobile Hotspot overview and change the settings to use 2.4 GHz only. Note that the free version of Hotspot Lite adds a Hotspot- prefix to the WiFi name.
| [1] | You can find the documentation under Configuration/Connect/Protocol/Web server |
| [2] | You can determine the device IP from your router’s ‘connected devices’ overview based on the device MAC address (found in the device.json) |